Karma exercises
As part of the Karmic Relationships lectures of 1924-05-GA236 (see below), Rudolf Steiner gave practical exercises for gaining insight into karmic connections. However he already included exercises in lectures much earlier, even if he was not go into these (as the conditions were not allowing to speak openly on these matters until 1924).
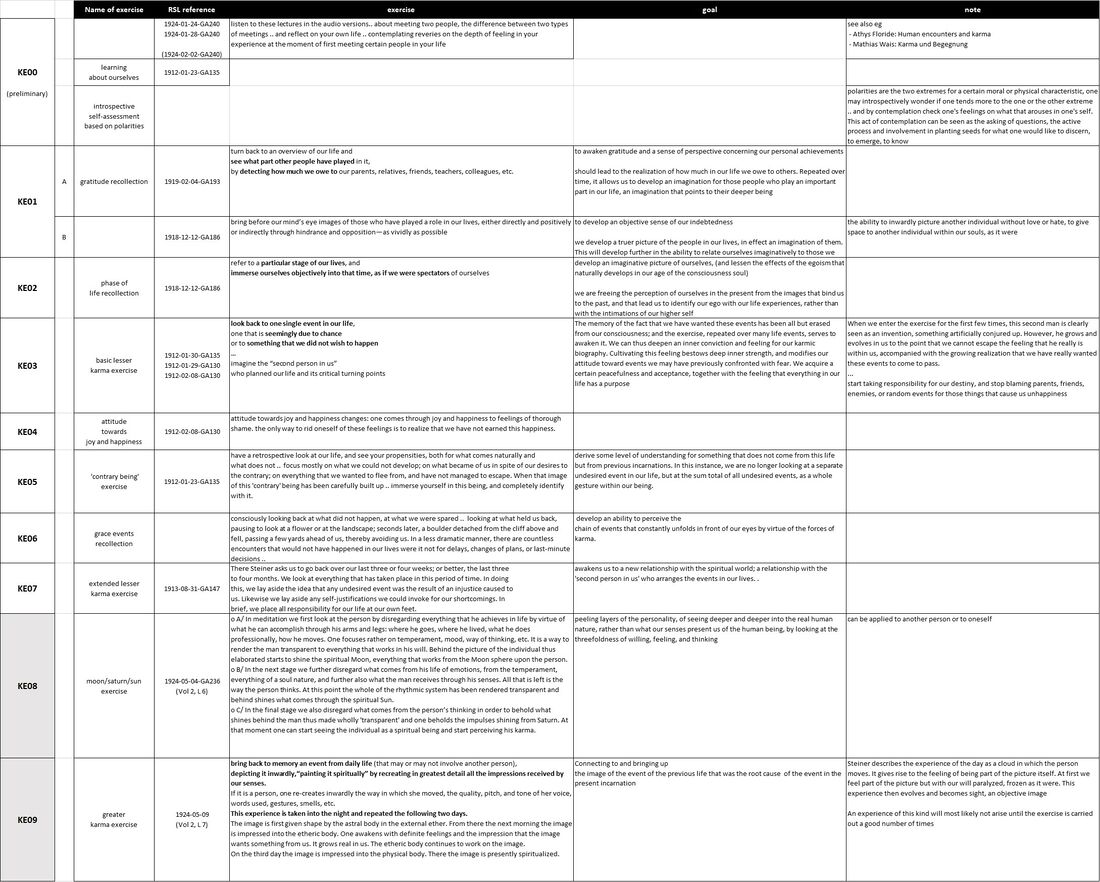
Schema FMC00.242 below groups these into ten main exercise categories that can be taken along in the practice of daily initiation exercises and/or biography work.
Aspects
- These exercises were grouped by Luigi Morelli as 'spirit recollection', see 'Further reading' section below.
- The practical exercises for the vision or perception of karma are given in two lectures: 1924-05-04-GA236 and 1924-05-09-GA236
Inspirational quotes
Franz Bardon
On Earth every human being has two teachers: firstly, him- or herself and, secondly, fate.
What Man is not able to achieve by his own diligence, practice, renunciation, pain, grief, etc., will be served up by the buffets of fate.
Life is a school, not an amusement fair.
1924-04-12-GA236
Truly the souls of men are far too rich in content to enable us to understand their content out of a single life alone.
from: KRI - Karmic Relationships Individualities#1924-04-12-GA236
Illustrations
Schema FMC00.242 provides an overview of exercises of self-reflection and spirit recollection to gain insight into karmic connections. As always on this site, double click the schema once to get the download page, twice to enlarge to full screen, three to zoom in further.
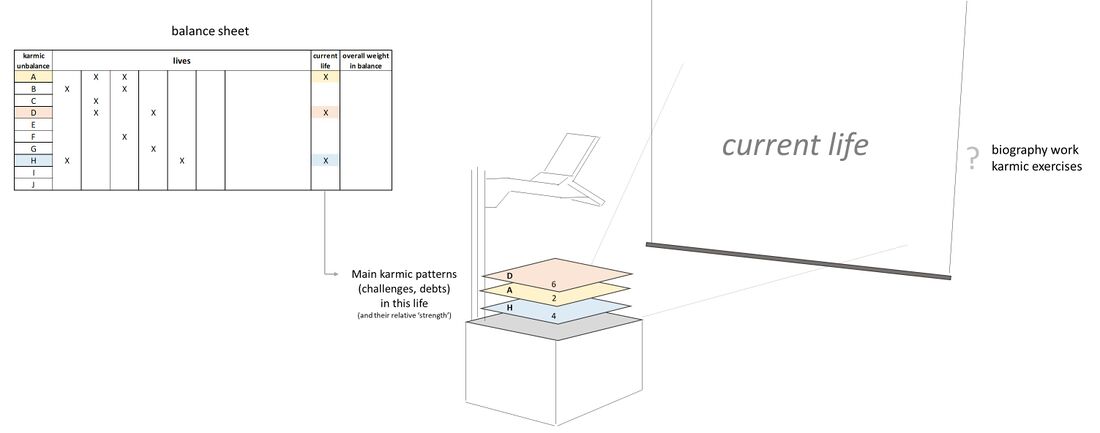
Schema FMC00.531 depicts a simple metaphoric image for the main karmic patterns, challenges and debts in one's life or incarnation.
On the upper left is represented the accounting 'balance sheet' of karmic unbalances as a result of many previous lives, the 'book of lives' (part of Man's higher spiritual self or Individuality), also called 'causal body' in theosophy. In the accounting image, each life delivers like the equivalent of 'annual results' that is added to the balance sheet in the process and journey between death and a new birth.
When we investigate our current life with biography work and karma exercises (on the right), we will find particularities, obvious or recurrent challenges, curious patterns. Some don't seem to belong in our experience of this current life, and/or may be an odd aspect of our Personality, even though we feel and have to acknowledge they are an intrinsic part of our true self (and Individuality). Depending on the individual, the process may include spontaneous Past life memories, whereby certain karmic patterns may clearly point to a particular previous incarnation. Importantly, the patterns are typically interwoven with relationships with key people in our lives (their role, impact, the period of our life) see Karmic relationships.
Rudolf Steiner gave examples of the above with the Karma research case studies about the KRI - Karmic Relationships Individualities.
During the journey between death and a new birth, before incarnating the soul develops a life plan in the spiritual world, and so each life has a selection of challenges to work and balance out these karmic unbalances - see a.o. Schema FMC00.287. The image of the slide projector depicts how patterns seen in one life stem from elements from various previous lives shown here as overlay slides.
Initiation is the process of fast tracking this process (versus the 'wheel of karma') by taking on this work on our human character consciously during incarnate life with daily initiation exercises.
Lecture coverage and references
1912-01-23-GA135
It is good to look back on one's life in a certain way, and above all to envisage clearly those things that one did not like. All this leads to a more intimate knowledge of the inner kernel of our being. For example, a son who would have liked to become a poet was destined by his father to be a craftsman, and a craftsman he became, although he would sooner have been a poet. It is well to know clearly what we really wanted to be, and what we have become against our will, to visualise what would have suited us in the time of our youth but was not our lot, and then, again, what we would have liked to avoid.
All that I am saying refers, of course, to life in the past, not in the future — that would be a false conception. We must therefore be quite clear as to what such a retrospect into the past means; it tells us what we did not want, what we would have liked to avoid. When we have made that clear to ourselves, we really have a picture of those things in our life which have pleased us least. That is the essential point. And we must now try to live into a very remarkable conception: we must desire and will everything that we have not desired or willed. We must imagine to ourselves: What should I actually have become if I had ardently desired everything that in fact I did not wish for and which really went against the grain in life? In a certain sense we must here rule out what we have succeeded in overcoming, for the most important thing is that we should ardently wish or picture ourselves wishing for the things we have not desired, or concerning which we have not been able to carry out our wishes, so that we create for ourselves, in feeling and thought, a being hitherto unfamiliar to us. We must picture ourselves as this being with great intensity. If we can do this, if we can identify ourselves with the being we have ourselves built up in this way, we have made some real progress towards becoming acquainted with the inner soul-kernel of our being; for in the picture we have thus been able to make of our own personality there will arise something that we have not been in this present incarnation but which we have introduced into it. Our deeper being will emerge from the picture built up in this way.
You will see, therefore, that from those who wish to gain knowledge of this inner kernel of being, something is required for which people in our age have no inclination at all. They are not disposed to desire anything of the sort, for nowadays, if they reflect upon their own nature, they want to find themselves absolutely satisfied with it as it is. When we go back to earlier, more deeply religious epochs, we find there a feeling that man should feel himself overwhelmed because he so little resembled his Divine Archetype. This was not, of course, the idea of which we have spoken to-day, but it was an idea which led man away from what usually satisfies him, to something else, to that being which lives on beyond the organism existing between birth and death, even if it did not lead to the conviction of another incarnation. If you call up the counterpart of yourself, the following thought will dawn upon you. This counterpart — difficult as it may be to realise it as a picture of yourself in this life — is nevertheless connected with you, and you cannot disown it. Once it appears, it will follow you, hover before your soul and crystallise in such a way that you will realise that it has something to do with you, but certainly not with your present life. And then there develops the perception that this picture is derived from an earlier life.
1912-01-29-GA130
If we pass over our life in review and make real efforts to get to the root of its happenings, very much can be gained. We shall recognise the justice of many things in our destiny and realise that we have deserved them. — Suppose someone has been frivolous and superficial in the present incarnation and is subsequently struck by a blow of fate. It may not be possible, externally, to connect the blow of fate directly with the frivolousness, but a feeling arises, nevertheless, that there is justice in it. Further examination of life will reveal blows of fate which we can only attribute to chance, for which we find no explanation whatever. These two categories of experiences are to be discovered as we look back over our life. Now it is important to make a clear distinction between apparent chance and obvious necessity. When a man reviews his life with reference to these two kinds of happenings, he will fail to reach any higher stage of development unless he endeavours to have a very clear perception of everything that seems to him to be chance. We must try, above all, to have clear perception of those things we have not desired, which go right against the grain. It is possible to induce a certain attitude of soul and to say to ourselves: How would it be if I were to take those things which I have not desired, which are disagreeable to me and imagine that I myself actually willed them? In other words, we imagine with all intensity that we ourselves willed our particular circumstances.
In regard to apparently fortuitous happenings, we must picture the possibility of having ourselves put forth a deliberate and strong effort of will in order to bring them about. Meditatively as it were, we must induce this attitude to happenings which, on the face of them, seem to be purely fortuitous in our lives. Every human being today is capable of this mental exercise. If we proceed in this way, a very definite impression will ultimately be made upon the soul; we shall feel as though something were striving to be released from us. The soul says to itself: “Here, as a mental image, I have before me a second being; he is actually there.” We cannot get rid of this image and the being gradually becomes our “Double.” The soul begins to feel a real connection with this being who has been imagined into existence, to realise that this being actually exists within us. If this conception deepens into a vivid and intense experience, we become aware that this “imagined” being is by no means without significance. The conviction comes to us: this being was already once in existence and at that time you had within you the impulses of will which led to the apparently chance happenings of today. Thereby we reach a deep-rooted conviction that we were already in existence before coming down into the body. Every human being today can have this conviction. — And now let us consider the question of the successive incarnations of the human being. What is it that reincarnates? How can we discover the answer to this question?
There are three fundamental and distinct categories of experiences in the life of soul. Firstly, our mental pictures, our ideas, our thoughts. In forming a mental picture, our attitude may well be one of complete neutrality; we need not love or hate what we picture inwardly, neither need we feel sympathy or antipathy towards it. Secondly, there are the moods and shades of feeling which arise by the side of the ideas or the thoughts; the cause of these moods in the life of feeling is that we like or love one thing, dislike or abhor another, and so forth. The third kind of experiences in the life of soul are the impulses of will. There are, of course, transitional stages but speaking generally these are the three categories. Moreover it is fundamentally characteristic of a healthy life of soul to be able to keep these three kinds of experiences separate and distinct from each other. Our life of thought and mental presentation arises because we receive stimuli from outside. Nobody will find it difficult to realise that the life of thought is the most closely bound up with the present incarnation. This, after all, is quite obvious when we bear in mind that speech is the instrument whereby we express our thoughts; and speech, or language, must, in the nature of things, differ in every incarnation. We no more bring language with us at the beginning of a new incarnation than we bring thoughts and ideas. The language as well as the thoughts must be acquired afresh in each incarnation. Hebbel once wrote something very remarkable in his diary. — The idea occurred to him that a scene in which the reincarnated Plato was being soundly chastised by the teacher for his lack of understanding of Plato would produce a very striking effect in a play! A man does not carry over his thought and mental life from one incarnation to another and takes practically nothing of it with him into his post-mortem existence. After death we evolve no thoughts or mental pictures but have direct perceptions, just as our physical eyes have perceptions of colour. After death, the world of concepts is seen as a kind of net stretching across existence. But our feelings, our moods of heart and feeling — these we retain after death and also bring their forces with us as qualities and tendencies of soul into a new earthly life. For example, even if a child's life of thought is undeveloped, we shall be able to notice quite definite tendencies in his life of feeling. And because our impulses of will are linked with feelings, we also take them with us into our life after death. If, for example, a man lends himself to fallacy and error, the effect upon his life of feeling is not the same as if he lends himself to truth. For a long time after death we suffer from the consequences of false mental presentations and ideas. Our attention must therefore turn to the qualities and moods of feeling and the impulses of the will, when we ask: What is it that actually passes on from one incarnation to another?
Suppose something painful happened to us ten or twenty years ago. In thought today we may be able to remember it quite distinctly and in detail. But the actual pain we felt at the time has all but faded away; we cannot re-experience the stirrings of feeling and impulses of will by which it was accompanied. Think for a moment of Bismarck and the overwhelming difficulties of which he was conscious in taking his decision to go to war in 1866; think of what tumultuous feelings, what teeming impulses of will were working in Bismarck at that time! But even when writing his memoirs, would Bismarck have been conscious of these emotions and resolves with anything like the same intensity? Of course not! Man's memory between birth and death is composed of thoughts and mental pictures. It may, of course, be that even after ten or twenty years, a feeling of pain comes over us at the recollection of some sorrowful event, but generally speaking the pain will have greatly diminished after this lapse of time; in thought, however, we can remember the very details of the event. If we now picture to ourselves that we actually willed certain painful events, that in reality we welcomed things which in our youth we may have hated, the very difficulty of this exercise rouses the soul and thus has an effect upon the life of feeling. Suppose, for example, a stone once crashed down upon us. — We now try with all intensity to picture that we ourselves willed it so. Through such mental pictures — that we ourselves have willed the chance events in our life — we arouse, in the life of feeling, memory of our earlier incarnations. In this way we begin to realise how we are rooted in the spiritual world, we begin to understand our destiny. We have brought with us, from our previous incarnation, the will for the chance events of this life.
To devote ourselves in meditation to such thoughts, and elaborate them, is of the highest importance. Between death and a new birth too, much transpires, for this period is infinitely rich in experiences — purely spiritual experiences, of course. We therefore bring with us qualities of feeling and impulses of will from the period between death and a new birth, that is to say, from the spiritual world. Upon this rests a certain occurrence of very great importance in the modern age, but one of which little notice is taken. The occurrence is to be found in the lives of many people today but usually passes by unnoticed. It is, however, the task of Anthroposophy to point to such an occurrence and its significance. Let me make it clear by an example. — Suppose a man has occasion to go somewhere or other and his path happens to take him in the wake of another human being, a child perhaps. Suddenly the man catches sight of a yawning chasm at the edge of the path along which the child is walking. A few steps farther and the child will inevitably fall over the edge into the chasm. He runs to save the child, runs and runs, entirely forgetting about the chasm. Then he suddenly hears a voice calling out to him from somewhere: “Stand still!” He halts as though nailed to the spot. At that moment the child catches hold of a tree and also stops, so that no harm befalls. If no voice had called at that moment the man must inevitably have fallen into the chasm. And now he wonders from whom the voice came. He finds no single soul who could have called, but he realises that he would quite certainly have been killed if he had not heard this voice; yet however closely he investigates he cannot find that the warning came from any physical voice.
In deep self-observation, many human beings living at the present time would be able to recognise a similar experience in their lives. But far too little attention is paid to such things. An experience of this kind may pass by without leaving a trace — then the impression fades away and no importance is attached to the experience. But suppose a man has been attentive and realises that it was not without significance. The thought may then occur to him: At that point in your life you were facing a crisis, a karmic crisis; your life should really have ended at that moment, for you had forfeited it. You were saved by something akin to chance and since then a second life has as it were been planted on the first; this second life is to be regarded as a gift bestowed upon you and you must act accordingly. When such an experience makes a man feel that his life, from that time onwards, has been bestowed upon him as a gift, this means that he can be accounted a follower of Christian Rosenkreutz. For this is how Christian Rosenkreutz calls the souls whom he has chosen. A man who can recall such an occurrence — and everyone sitting here can discover something of the kind in their lives if they observe closely enough — has the right to say to himself: Christian Rosenkreutz has given me a sign from the spiritual world that I belong to his stream. Christian Rosenkreutz has added such an experience to my karma. — This is the way in which Christian Rosenkreutz chooses his pupils; this is how he gathers his community. — A man who is conscious of this experience knows with certainty that a path has been pointed out to him which he must follow, trying to discover how he can dedicate himself to the service of Rosicrucianism. If there are some who have not yet recognised the sign, they will do so later on; for he to whom the sign has once been given will never again be free from it. — That such an experience comes to a man is due to the fact that during the period between his last death and his present birth, he was in contact with Christian Rosenkreutz in the spiritual world. It was then that Christian Rosenkreutz chose us, imparting an impulse of will which leads us, now, to such experiences. This is the way in which spiritual connections are established. Materialistic thought will naturally regard all these things as hallucinations, just as it regards the experience of Paul at Damascus as having been an hallucination. The logical conclusion to be drawn from this is that the whole of Christianity is based upon an hallucination, therefore upon error. For theologians are perfectly well aware that the Event at Damascus is the foundation-stone of the whole of subsequent Christianity. And if this foundation stone itself is nothing but an illusion, then, if thought is consistent, everything built upon it must obviously be fallacy
1912-01-30-GA135
A little self-knowledge will render many of life's happenings comprehensible to us. If something disagreeable happens and we do not fully see the reason for it, we may say to ourselves: “I really am a careless person, and it is no wonder this happened to me.” This shows at least some understanding of what has happened. There are, however, countless experiences in life of which we simply cannot conceive that they are connected with the forces and faculties of our soul. In ordinary life we usually speak of them as accidental. We speak of accidents when we do not perceive how the things that befall us as strokes of fate are connected with the inner leanings of our soul, and so forth. In the last lecture attention was drawn also to events of another kind — experiences through which in a sense we extricate ourselves, by means of what we generally call our Ego, from some situation we are in. For example: a man may be destined by his parents or near relations to a certain calling or position in life, and he feels he must at all costs leave it and do something else. When in later life we look back on something like this, we say to ourselves: “We were put into a certain position in life, but by our own impulse of will, by our personal sympathy or antipathy, we have extricated ourselves from it.”
The point is not to pay attention to all manner of things, but to confine ourselves in our retrospective memory to something that vitally affected our life. If, for instance, a man has never felt any desire, nor had any motive to become a sailor, a will-impulse such as was referred to in the last lecture does not come into consideration at all, but only one whereby he actually brought about a change of fate, a reversal of some situation in life. But when in later life we remember something of this kind and realise that we extricated ourselves, we should not cultivate any rueful feelings about it, as though we ought to have stayed where we were. The essential point is not the practical outcome of the decision, but the recollection of when such turning points occurred. Then with regard to events of which we say, “This happened by chance,” or “We were in such and such a position but have extricated ourselves from it,” we must evoke with utmost energy the following inner experience.
We say to ourselves: “I will imagine that the position from which I extricated myself was one in which I deliberately placed myself with the strongest impulse of will.” We bring before our own souls the very thing that was repugnant to us and from which we extricated ourselves. We do this in such a way that we say: “As an experiment I will give myself up to the idea that I willed this with all my might; I will bring before my soul the picture of a man who willed something like this with all his might.”
And let us imagine that we ourselves brought about the events called “accidents.” Suppose it has come back to our memory that at some place a stone fell from a building on to our shoulders and hurt us badly. Then let us imagine that we had climbed on to the roof and placed the stone so that it was bound to fall, and that then we ran quickly under it so that it had to fall on us. It is of no consequence that such ideas are grotesque; the point is what we want to acquire through them.
Let us now put ourselves right into the soul of a man of whom we have built up such a picture, a man who has actually willed everything that has happened to us “by accident,” who has desired everything from which we have extricated ourselves. There will be no result in the soul if we practise such an exercise two or three or four times only, but a great deal will result if we practise it in connection with the innumerable experiences which we shall find if we look for them. If we do this over and over again, forming a living conception of a man who has willed everything that we have not willed we shall find that the picture never leaves us again, that it makes a very remarkable impression on us, as though it really had something to do with us. If we then acquire a certain delicate perception in this kind of self-probation, we shall soon discover how such a mood and such a picture, built up by ourselves, resemble an image we have called up from memory. The difference is only this, that when we call up such an image from memory in the ordinary way, it generally remains simply an image, but when we practise the exercises of which we have been speaking, what comes to life in the soul has in it an element of feeling, an element connected more with the moods of the soul, and less with images. We feel a particular relationship to this picture. The picture itself is not of much account, but the feelings we have make an impression similar to that made by memory-images. If we repeat this process over and over again, we arrive through an inner clarification at the ‘knowledge,’ one might say, that the picture we have built up is becoming clearer and clearer, just as a memory-image does when one starts to recall it out of dark depths of the soul.
Thus it is not a question of what we imagine, for this changes and becomes something different. It goes through a process similar to that which occurs when we want to remember a particular name and it nearly comes and then goes; we have a partial recollection of it and then say, for instance, Nuszbaumer, yet we have a feeling that this is not quite right, and then, without our being able to say why, the right name comes to us — Nuszdorfer, perhaps. Just as here the names Nüszbaumer, Nüszdorfer, build each other up, so the picture rights itself and changes. This is what causes the feeling to arise: “Here I have attained something which exists within me, and by the way it exists within me and is related to the rest of my soul-life, it plainly shows me that it cannot have existed within me in this form in my present incarnation!” So we perceive with the greatest inner clarity that what exists within us in this form, lies further back. Only we must realise that we are here dealing with a kind of faculty of remembrance which can be developed in the human soul, a faculty which, in contradistinction to the ordinary faculty of remembrance, must be designated by a different name. We must designate the ordinary faculty of remembrance as “image-memory,” but the faculty of remembrance now in question must really be described as a kind of “feeling and experience memory.” That this has a certain foundation can be proved by the following reflections.
We must bear in mind that our ordinary faculty of remembrance is really a kind of image-memory. Think how a specially painful event that perhaps happened to you twenty years ago, reappears in memory. The event may come up before you in all its details, but the pain which you suffered is no longer felt to the same extent; it is in a sense blotted out of the memory-image. There are, of course different degrees, and it may well happen that something has struck a man such a blow that again and again a fresh and more intense sorrow is felt when he remembers the experience. The general principle, however, holds good: so far as our present incarnation is concerned our faculty of remembrance is an image-memory, whereas the feelings that were experienced, or the will-impulses themselves, do not arise again in the soul with anything like the same intensity.
1912-02-08-GA130
It is difficult, however, to come to terms with joy and happiness. Much as we may accept the attitude that we have wanted our suffering, when we apply the same attitude to joy and happiness, we cannot but feel ashamed of ourselves. A deep feeling of shame will be experienced. The only way to overcome this feeling is to realize that we were not the ones who gave ourselves our joys and happiness through the law of karma. This is the only cure as, otherwise, the feeling of shame can become so intense that it virtually destroys us in our souls. Relief can only be found by not making the wiser man in us responsible for having driven us toward our joys. With this thought, one will feel that one hits the truth, because the feeling of shame will disappear. It is a fact that our joy and happiness come to us in life as something that is bestowed upon us, without our participation, by a wise divine guidance, as something we must accept as grace, as something that is to unite us with the universe. Happiness and joy shall have such an effect upon us in the sacred moments in our lives and in our intimate hours of introspection that we shall experience them as grace, as grace from the divine powers of the world who want to receive us and who, as it were, embed us in their being.
While our pain and suffering lead us to ourselves and make us more genuinely ourselves, we develop through joy and happiness, provided that we consider them as grace, a feeling that one can only describe as being blissfully embedded in the divine forces and powers of the world. Here the only justified attitude toward happiness and joy is one of gratitude. Nobody will understand joy and happiness in the intimate hours of self-knowledge when he ascribes them to his karma. If he involves karma, he commits an error that is liable to weaken and paralyze the spiritual in him. Every thought to the effect that joy and happiness are deserved actually weakens and paralyzes us. This may be a hard fact to understand because everyone who admits that his pain is inflicted upon himself by his own individuality would obviously expect to be his own master also with regard to joy and happiness. But a simple look at life can teach us that joy and happiness have an extinguishing power. Nowhere is this extinguishing effect of joy and happiness better described than in Goethe's Faust in the words, “And thus I stagger from desire to pleasure. And in pleasure I am parched with desire.” Simple reflection upon the influence of personal enjoyment shows that inherent in it is something that makes us stagger and blots out our true being.
No sermon is here being delivered against enjoyment, nor is an invitation extended to practice self-torture, or to pinch ourselves with red hot pliers, or the like. If one recognizes a situation in the right way, it does not mean that one should escape from it. No escape, therefore, is suggested, but a silent acceptance of joy and happiness whenever they appear. We must develop the inner attitude that we experience them as grace, and the more the better. Thus do we immerse ourselves the more in the divine. Therefore, these words are said not in order to preach asceticism, but in order to awaken the right mood toward joy and happiness.
If it is thought that joy and happiness have a paralyzing and extinguishing effect, and that therefore man should flee from them, then one would promote the ideal of false asceticism and self-torture. In this event, man, in reality, would be escaping from the grace that is given to him by the gods. Self-torture practiced by ascetics, monks and nuns is nothing but a continuous rebellion against the gods. It behooves us to feel pain as something that comes to us through our karma. In joy and happiness, we can feel that the divine is descending to us.
May joy and happiness be for us a sign as to how close the gods have attracted us, and may our pain and suffering be a sign as to how far removed we are from what we are to become as good human beings. This is the fundamental attitude toward karma without which we cannot really move ahead in life. In what the world bestows upon us as goodness and beauty, we must conceive the world powers of which it is said in the Bible, “And he looked at the world and he saw that it was good.” But inasmuch as we experience pain and suffering, we must recognize what man has made of the world during its evolution, which originally was a good world, and what he must contribute toward its betterment by educating himself to bear pain with purpose and energy.
What has now been described are two ways to confront karma. To a certain extent, our karma consists of suffering and joys. We relate ourselves to our karma with the right attitude when we can consider it as something we really wanted and when we can confront our sufferings and joys with the proper understanding. But a review of karma can be extended further, which we shall do today and tomorrow.
Karma not only shows us what is related to our lives in a joyful and painful manner. But as the result of the working of karma, we meet many people during the course of our lives with whom we only become slightly acquainted, and people with whom we are connected in various ways during long periods of our lives as relatives and friends. We meet people who either cause us pain directly, or as a result of some joint undertaking that runs into obstructions. We meet people who are helpful, or to whom we can be helpful. In short, many relationships are possible. If the effects of karma, as described.the day before yesterday, are to become fruitful, then we must accept the fact that the wiser man in us wants certain experiences. He seeks a person who seems accidentally to cross our paths. He is the one who leads us to other people with whom we get engaged in this or that way. What is really guiding this wiser man in us when he wants to meet this or that person? What is he basing himself on? In answer, we have to say to ourselves that we want to meet him because we have met him previously. It may not have happened in the last life; it could have happened much earlier. The wiser man in us leads us to this person because we had dealings with him in a previous life, or because we may have incurred a debt in one way or another. We are led to this person as though by magic.
and about happinstance, human encounters:
- The people with whom we meet, and the acquaintances we make in the middle period of our lives are curiously enough the very people with whom we were engaged during the period of early childhood in one of our previous incarnations. It is an established fact that, as a general rule, although not always, we meet in the middle period of our lives, as a result of karmic guidance, the very people who were once our parents. It is unlikely that we meet in early childhood the persons who were once our parents. This happens during the middle of life. This may appear as a strange fact, but this is the way it is. When we attempt to apply such rules to the experience of life, and when we direct our thoughts accordingly, then we can learn a great deal. When a person at about the age of thirty establishes a relationship to another, either through the bonds of love or of friendship, or when they get involved in conflict, or in any other experience, we will understand a great deal more about these relationships if we consider hypothetically that the person may have once been related to the other as a child is to his parents.
- The very people with whom we have been associated in our early childhood, such as parents, sisters and brothers, playmates and other companions, as a rule are the very people whom we have met in the previous or one of our previous incarnations around our thirtieth year. These people frequently appear as our parents, sisters or brothers in the present incarnation.
- You may now ask what the relation is to the people we meet during the declining curve of our lives. We have discovered that at the beginning of our lives, we meet people with whom we were acquainted during the middle period of a previous life, while now during the middle of our lives, we recognize those with whom we were involved at the beginning of previous existences.
But how about the period of our descending life? The answer is that we may be led to people with whom we were involved in a previous life, or we may not yet have been involved with them.
- They will have been connected with us in a previous life if we are meeting under special circumstances that occur at decisive junctures of a life span, when, for example, a bitter disappointment confronts us with a serious probation. In such a situation, it is likely that we are meeting during the second period of our lives people with whom we were previously connected. Thereby conditions are dislodged and experiences that were caused in the past can be resolved. Karma works in many ways and one cannot force it into definite patterns. But as a general rule, it can be stated that during the second half of our lives we encounter people with whom the karmic connections that are beginning to be woven cannot be resolved in one life. Let us assume that we have caused suffering to someone in a previous life. It is easy to assume that the wiser man in us will lead us back to this person in a subsequent life in order that we may equalize the harm that we have done. But life conditions cannot always permit that we can equalize everything, but perhaps only a part of it. Thereby matters are complicated, and it becomes possible that such a remainder of karma may be corrected in the second half of life. Looking at it this way, we are placing our connections and communications with other people in the light of this karma.
1913-08-31-GA147
A good exercise for someone striving in the spiritual sphere would be to say every so often something like this: “I will think back over the last three or four weeks — or better still, months — letting all the important happenings in which I was involved pass before my inner eye. I will deliberately disregard whatever injustice may have been done to me. I will omit all the excuses for my difficulties that I've expressed so frequently, such as, for instance: it was someone else's fault. I will not for a moment consider that any other person could have been to blame but I myself.” When we reflect on how constantly we are inclined to make others and not ourselves responsible for what we don't like, we will be able to judge how valuable such a review of our life can be, in which we knowingly eliminate thoughts of injustice done to us and in which we do not allow criticism or blame of another person to arise. If you undertake such an exercise, you will discover that you are gaining a totally new relationship to the spiritual world. Such an effort will bring about a great change in the disposition and mood of one's soul. In seeking the path to clairvoyance, the extreme difficulty of entering the higher worlds without danger, as we have said repeatedly, shows how essential it is not to come apart, not to fall to pieces, when we have to “put our head into the ant hill.” We need then an immensely strengthened consciousness of self, such as a person may not develop in the physical world if he is not to be a rank egoist. In higher worlds, however, if he wants to maintain himself, stay aware of himself, realize himself, he must enter those worlds with an intensified feeling of self. Then, on coming back to the sense world, he must also have the ability to do away with this consciousness of self, in order not to be a thoroughgoing egoist. Thus, two contrasting statements can be made: in the higher worlds of spiritualities, man needs a strengthened consciousness of self; but in contrast, despite the strong feeling of self that one must find in the spirit world, what one must find in the physical world is that the spirit must come to life in a particular way: in all that one can describe as love in the physical world, the capacity for love, for sympathy and compassion, for the sharing of joys and sorrows.
1918-12-12-GA186
One is that we frequently attempt to look back over our present incarnation to survey what has happened to us in this life through our relations with others. If we are honest in this, most of us will say: Nowadays we generally regard the entrance of many people into our life in such a way that we see ourselves, our own personalities, as the center of the review. What have we gained from this or that person who has come into our life? This is our natural way of feeling. It is exactly this which we must try to combat. We should try in our souls to think of others, such as teachers, friends, those who have helped us and also those who have injured us (to whom we often owe more than to those who, from a certain point of view, have been of use to us). We should try to allow these pictures to pass before our souls as vividly as possible in order to see what each has done.
We shall see, if we proceed in this way, that by degrees we learn to forget ourselves, that in reality we find that almost everything which forms part of us could not be there at all unless this or that person had affected our lives, helping us on or teaching us something. When we look back on the years in the more distant past to people with whom we are no longer in contact and about whom it is easier to be objective, then we shall see how the soul-substance of our life has been created by the people and circumstances of the past. Our gaze then extends over a multitude of people whom we have known in the course of time. If we try to develop a sense of the debt we owe to this or that person — if we try to see ourselves in the mirror of those who have influenced us in the course of time, and who have been associated with us — then we shall be able to experience the opening-up of a new sense in our souls, a sense which enables us to gain a picture of the people whom we meet even in the present, with whom we stand face to face today. This is because we have practiced developing an objective picture of our indebtedness to people in the past. It is tremendously important that the impulse should awaken in us, not merely to feel sympathy or antipathy towards the people we meet, not merely to hate or love something connected with the person, but to awaken a true picture of the other in us, free from love or hate.
Perhaps you will not feel that what I am saying now is extremely important — but it is. For this ability to picture the other in oneself without love or hate, to allow the other individual to appear again within our soul, this is a faculty which is decreasing week by week in the evolution of humanity. It is something which men are, by degrees, completely losing. They pass one another by without arousing any interest in each other. Yet this ability to develop an imaginative faculty for the other is something that must enter into pedagogy and the education of children. For we can really develop this imaginative faculty in us if, instead of striving after the immediate sensations of life as is often done today, we are not afraid to look back quietly in our soul and see our relationships to other human beings. Then we shall be in a position to relate ourselves imaginatively to those whom we meet in the present. In this way we awaken the social instinct in us against the anti-social which quite unconsciously and of necessity continues to develop. This is one side of the picture.
The other is something that can be linked up with this review of our relations to others. It is when we try to become more and more objective about ourselves. Here we must also go back to our earlier years. Then we can directly, so to speak, go to the facts themselves. Suppose you are 30 or 40 years of age. You think, “How was it with me when I was ten years old? I will imagine myself entirely into the situation of that time. I will picture myself as another boy or girl of ten years old. I will try to forget that I was that; I will really take pains to objectify myself.” This objectifying of oneself, this freeing of oneself in the present from one's own past, this shelling-out of the Ego from its experiences, must be specially striven for in our present time. For the present has the tendency towards linking up the Ego more and more with its experiences.
Nowadays man wants to be instinctively that which his experiences make him. For this reason it is so very difficult to acquire the activity which Spiritual Science gives. The spirit must make a fresh effort each time. According to true occult science, nothing can be done by comfortably remaining in one's position. One forgets things and must always be cultivating them afresh. This is just as it should be because fresh efforts need to continually be made. He who has already made some progress in the realm of Spiritual Science attempts the most elementary things every day; others are ashamed to pay attention to the basics. For Spiritual Science, nothing should depend on remembering, but on man's immediate experience in the present. It is therefore a question of training ourselves in this faculty — through making ourselves objective — that we picture this boy or girl as if he or she were a stranger at an earlier time in our lives; of bestirring ourselves more and more, of getting free of events, and of being less haunted at 30 by the impulses of a 10 year old. Detachment from the past does not mean denial of the past. We gain it in another way again, and that is what is so important. On the one hand, we cultivate the social instinct and impulses in us by looking back upon those who have been connected with us in the past and regarding our souls as the products of these persons. In this way we acquire the imagination for meeting people in the present. On the other hand, through objectifying ourselves we gain possibilities of developing imagination directly. This objectifying of our earlier years is fruitful insofar as it does not work in us unconsciously. Think for a moment: If the 10 year old child works on unconsciously in you, then you are the 30 or 40 year old augmented by the 10 year old. It is just the same with the 11, the 12 year old child and so on. Egoism has tremendous power, but its power is lessened when you separate the earlier years from yourself and when you make them objective. This is the important point on which we must fix our attention.
1919-02-04-GA193
Today human beings are in a certain sense driven apart, and they have to seek quite a different relationship to one another. But first they have to learn about this. From a purely external point of view you can see everywhere that one human being knows very little about another. Spiritual Science is only beginning to show how human nature and human worth stand in their cosmic setting. In daily life one man knows little about another; he does not penetrate into the depths of his fellow man's soul. That is the general rule. Through a deepening of social life a new understanding of man must be found, and must permeate human development.
Instead of having eyes only for the man of flesh, apprehending him in a naturalistic way, devoid of the spirit, we must reach the stage of a spirit-filled social organism, wherein the activity of the gods in other men can be recognised.
But we shall not attain to this unless we do something about it. One thing we can do is to strive to deepen our own life of soul. There are many paths to that. I will mention only one, a meditative path. From various points of view, and with various aims, we can cast a backward glance over our own lives. We can ask ourselves: How has this life of mine unfolded since childhood? But we can do this also in a special way. Instead of bringing before our gaze what we ourselves have enjoyed or experienced, we can turn out attention to the persons who have figured in our lives as parents, brothers and sisters, friends, teachers and so on, and we can summon before our soul the inner nature of each of these persons, in place of our own. After a time we shall find ourselves reflecting how little we really owe to ourselves, and how much to all that has flowed into us from others. If we honestly build up this kind of self-scrutiny into an inner picture, we shall arrive at quite a new relationship to the outer world. From such a backward survey we retain certain feelings and impressions. And these are like fertile seeds planted in us — seeds for the growth of a true knowledge of man. Whoever undertakes again and again this inward contemplation, so that he recognises the contribution which other persons, perhaps long dead or far distant, have made to his own life, then when he meets another man, and establishes a personal relationship with him, an imagination of the other man's true being will rise before him.
This is something which must emerge as an inward and truly heartfelt social demand, bound up with this present time and necessary to the future development of mankind. So must Spiritual Science reveal its practical power to kindle and enrich human life.
This subject has a further aspect. In earlier times all self-knowledge, all introspection, was a much simpler affair, for a deeply inward social impulse is now emerging — and not only because of the enhanced awareness of some people concerning property or poverty. This impulse shows itself, for example, in the following way. Nowadays we pay very little attention to the fact that throughout life a constant process of ripening goes on. Inwardly honest men, such as Goethe, feel this. Even in his latest years Goethe was still eager to learn. His inward growth continued; he felt he had not finished with the task of becoming a man. And in looking back on his youth and prime he saw in all that had come to him then a preparation for the experiences brought by old age. Nowadays people very seldom think in that way — least of all when taking account of man as a social being. Everyone, as soon as he is twenty, wants to belong to some corporate body and — in the favourite phrase — to exercise his democratic judgment! It never occurs to anyone that there are things in life worth waiting for, because increasing ripeness comes with the years. Men to-day have no idea of that!
That is one thing we must learn, my dear friends — that all stages of life — and not only the first two or three decades of youth — bring gifts to man.
And there is something else we must learn. We are not concerned only with ourselves, but with people at other stages of life; and particularly with children, as they are born and grow up. A consequence of human evolution is that much which used to unfold of itself in the soul now has to be attained by extraordinary exertion — by a striving for super-sensible knowledge, or at least for a real knowledge of life. It is the same with the child as with people in general — a great deal in his own being remains hidden from him. And this applies not only to the experiences that will come in later life. A great deal that was formerly revealed through atavistic clairvoyance now remains hidden from a person who pays attention only to himself, who seeks for knowledge only within himself. It remains hidden from the cradle to the grave. This is also a consequence of the state of consciousness belonging to our age. We can strive for clear insight, yet much remains hidden — and precisely in the realm where we need to see clearly. This is a special characteristic of our time: we enter the world as children, bearing some quality which is important for the world, for the social life of humanity, for the understanding of history. But we cannot reach a knowledge of this, not in childhood, or in maturity, or in old age, if we remain shut up in ourselves. Knowledge of it, however, can be reached in a different way. We can reach it if we look at the child with finely-tuned spiritual perception, and realise that in the child is revealed something which the child does not and cannot ever know, but which can be understood by the soul of another person who in old age gazes on the child. It is something revealed through the child — not to the child himself and not to the man or woman whom the child becomes — but to the other person who from a later age looks with real love on his youngest contemporaries.
1924-05-04-GA236
1924-05-09-GA236
The greater karma exercise is in the second: Insight into karmic connections can be stimulated by picturing vividly something experienced during the day; during the night the astral body gives shape to the picture in the outer ether which impregnates it with its own substance; the picture is further elaborated during the second and third days and nights by the etheric body and it is then received into the physical body, spiritualised and transformed. Spiritual exertion is essential if will is to be transformed into vision. In the study of karma, absolute clarity and soundness of head and heart must prevail.
Discussion
Related pages
References and further reading
- Christoph Lindenberg: Praktische Karmaübungen: Grundlagen der Anthroposophie (1981) (article in Die Drei nr 51, 9, blz 601-608)
- Working with destiny - The practice of karma research - GoldenBlade (1997) - PDF download
- includes ao Nick Thomas: 'Karma research'; 'Intimations in images'
- Luigi Morelli (all the below are freely downloadable in PDF form online)
- Steiner's karma exercises
- Spirit recollection
- Karl Julius Schröer and Rudolf Steiner: Anthroposophy and the Teachings of Karma and Reincarnation
- Lili Chavannes, Ate Koopmans, Paul Wormer, Nothart M. Rohlfs: 'Blick aufs Karma: Schicksalselemente im Lebenslauf' (2004)
- Ate Koopmans, Rudolf Steiner: 'De karmaoefening voor de dag (2013)
- 1924-05-04-GA236 plus essay Ate Koopmans
- Robert Sardello:
- Guide to Experiencing Destiny: How to Detect the Time Current of the Future (2019)
- Experiencing Destiny (2020)
Various unqualified
- Jostein Sæther (°1954)
- 'Living with Invisible People' (2001 in EN, original in DE 1999 as 'Wandeln unter unsichtbaren Menschen: Eine karmische Autobiographie')
- Einstimmen aufs Karma: ein Wegbegleiter durch dynamische Meditation zu karmischen Hellsehen (2008)